Electronics Recycling in Ontario
How to Recycle Electronics and Electrical Equipment
Electronic waste (e-waste) Recycling
Let’s explore the step-by-step process of e-waste recycling
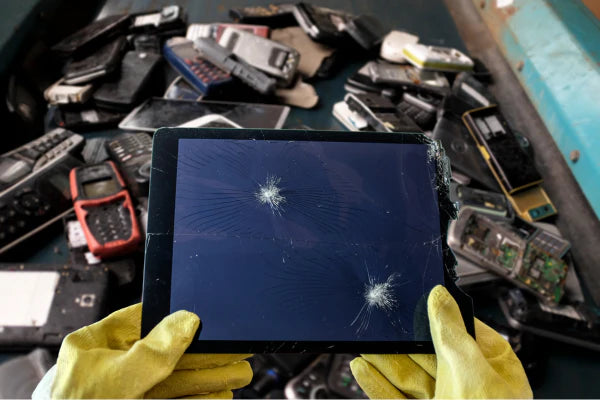

separating e-waste
Sorting and Shredding
- The journey begins with collecting electronic products through take-back programs, or designated collection points.
- At specialized electronics recycling facilities, workers manually sort and separate different types of e-waste. They examine items to identify reusable parts or components.
- E-waste then undergoes shredding. Powerful machines break down electronics into smaller pieces.
- This step prepares the materials for further processing.
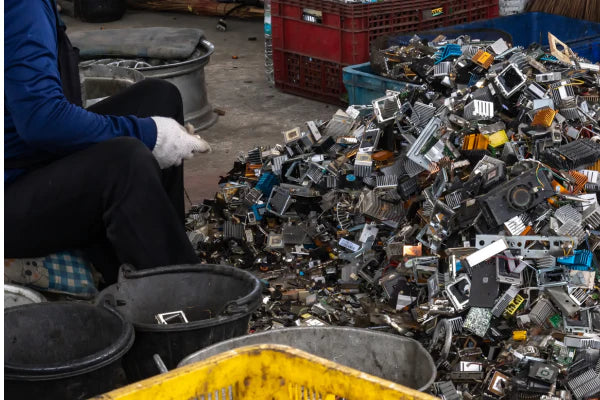

Metallic and Nonmetallic Separation
Removal, and Separation
- Magnets are employed to extract ferrous metals (such as iron and steel) from the shredded e-waste.
- These metals can be recycled separately.
- The remaining mixture is subjected to mechanical separation.
- Techniques like air classifiers and vibrating screens separate metallic components (like copper, aluminum, and gold) from nonmetallic ones (such as plastics and glass).
- Water-based separation is used to further segregate materials as plastic floats.

Keep our gadgets out of landfills and in the recycling loop
Special E-Waste Information
- CRT Recycling Process: Cathode ray tubes (CRTs) from old TVs and monitors require specialized handling due to their lead content.
- Importance of E-Waste Recycling: Proper recycling prevents toxic substances (like lead, cadmium, and mercury) from leaching into soil, water, and air. It also reduces health risks and conserves resources.
Frequently Asked Questions
In Ontario, you can dispose of electronics by taking them to designated e-waste recycling locations, participating in collection events, or using curbside pickup services offered by some municipalities. Ensure that you follow local guidelines for proper disposal.
E-waste can be taken to various locations, including municipal recycling centers, designated drop-off sites, and special e-waste collection events. Check local government websites for specific locations and schedules.
In Ontario, a wide range of electronics can be recycled, including computers, laptops, televisions, smartphones, and printers. Always verify with local recycling programs for specific guidelines on acceptable items.